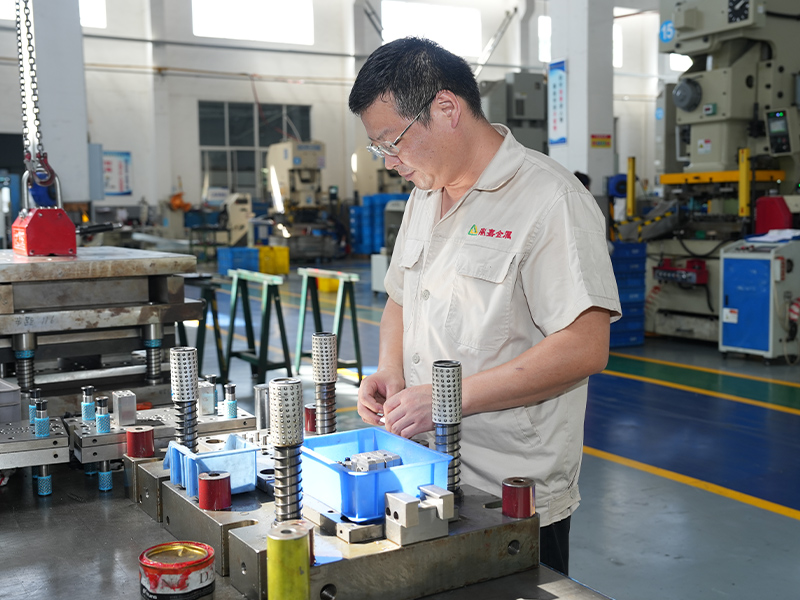
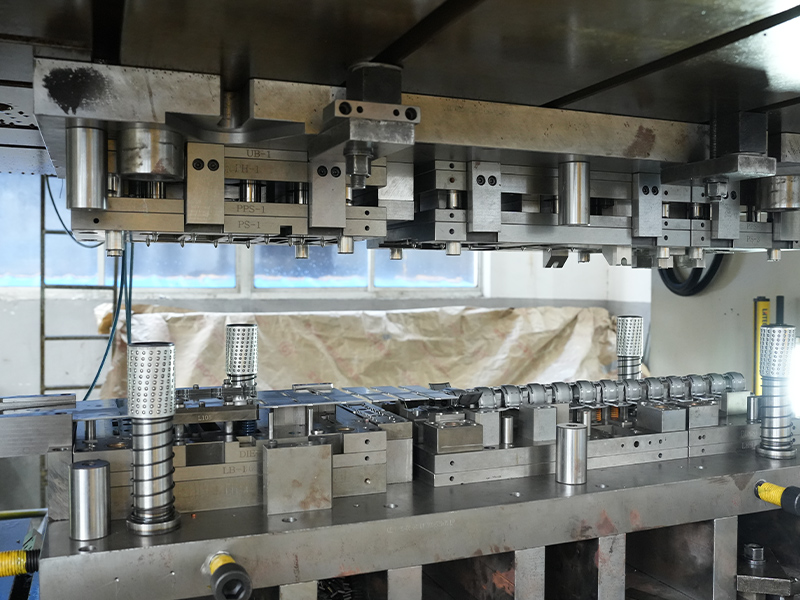
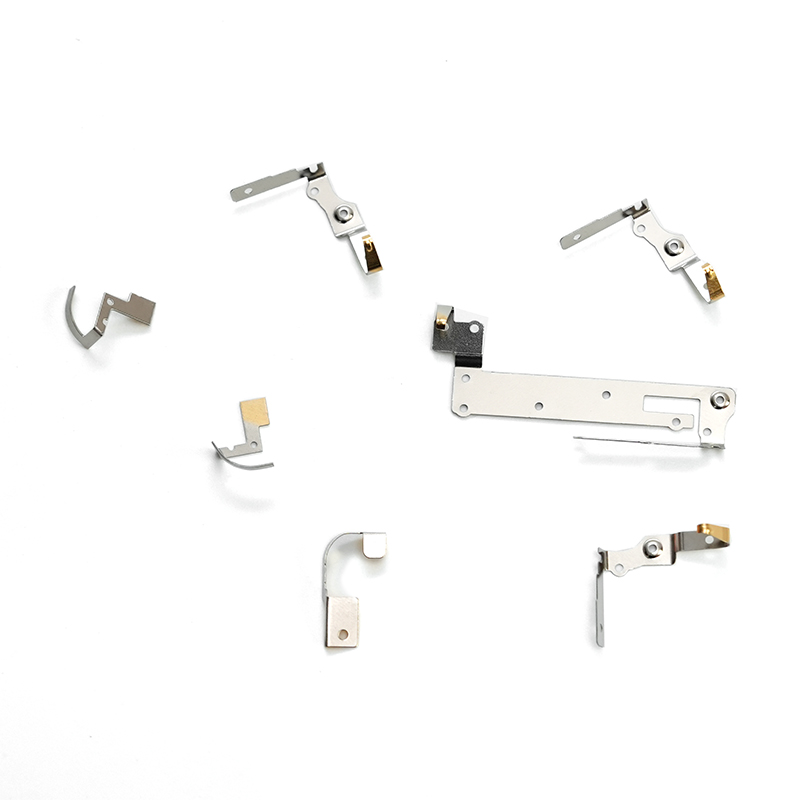
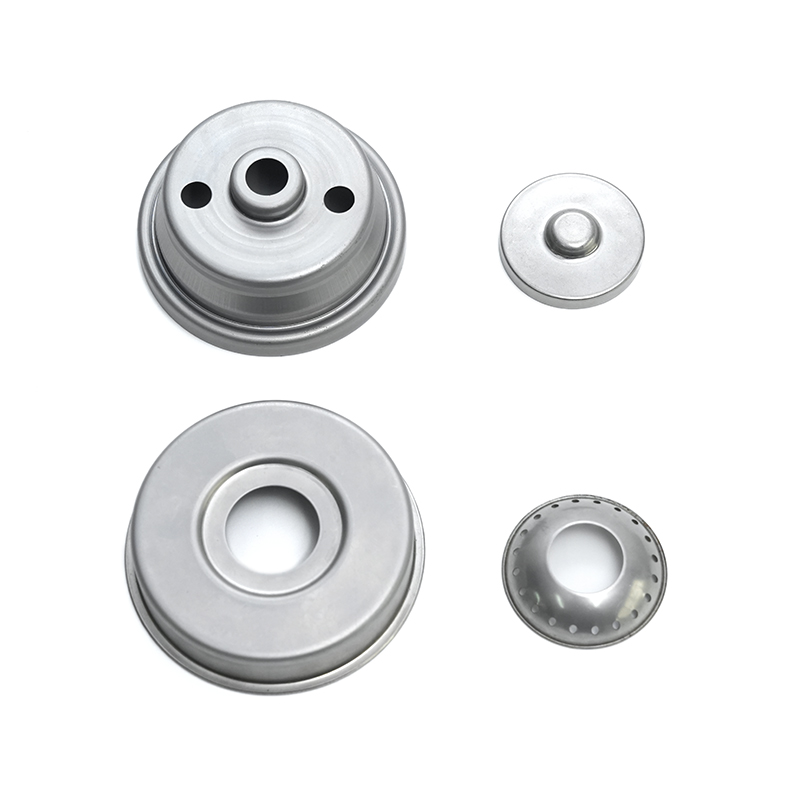
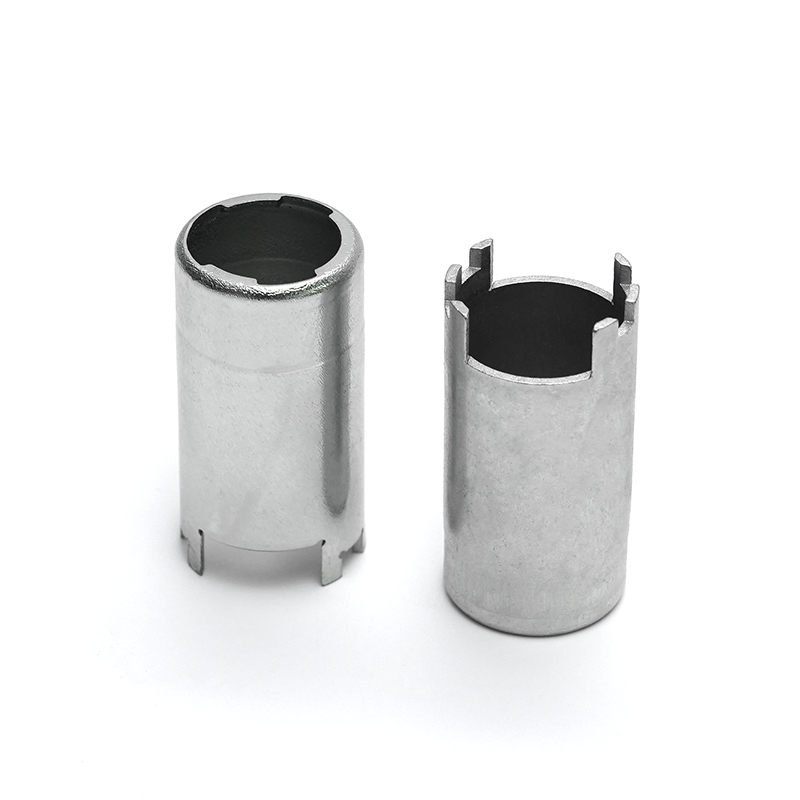
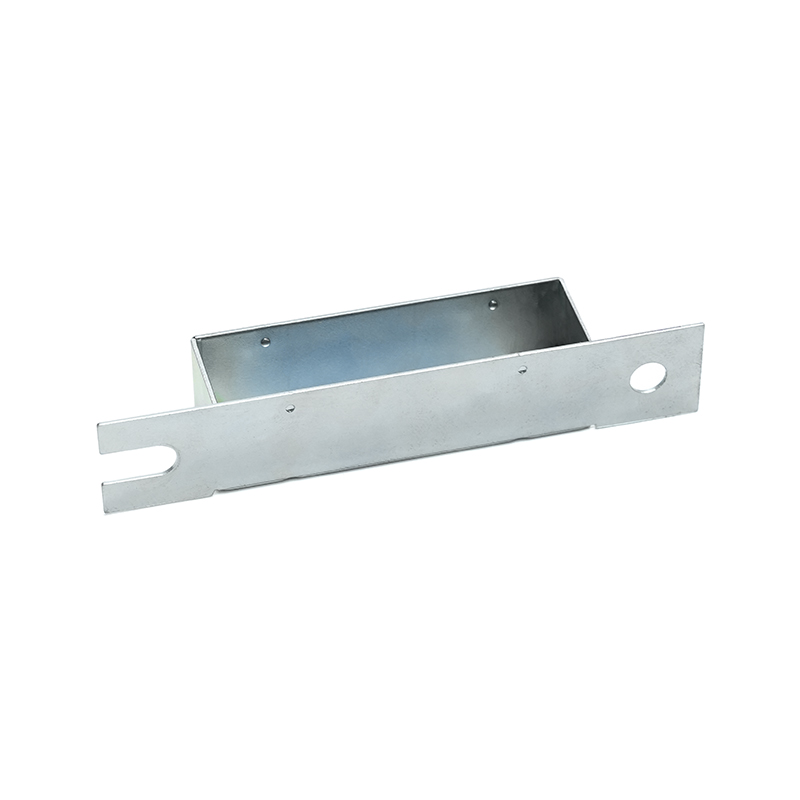
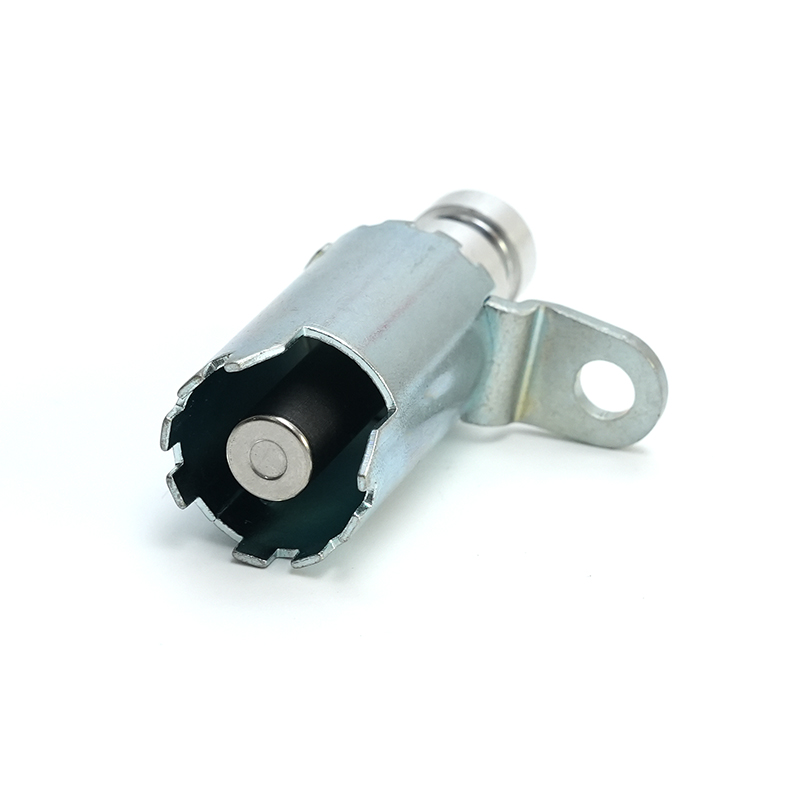
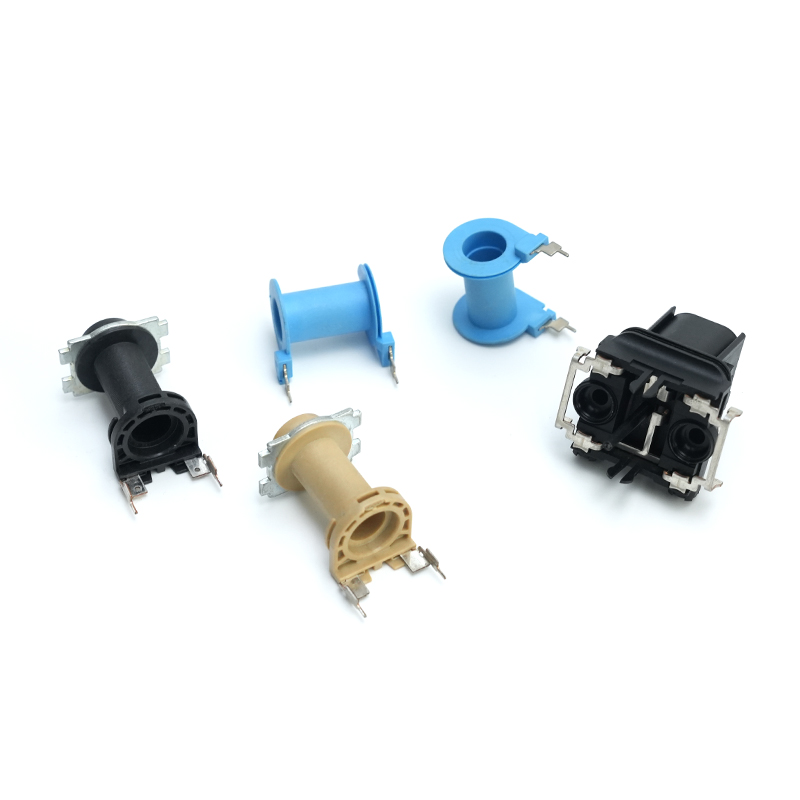
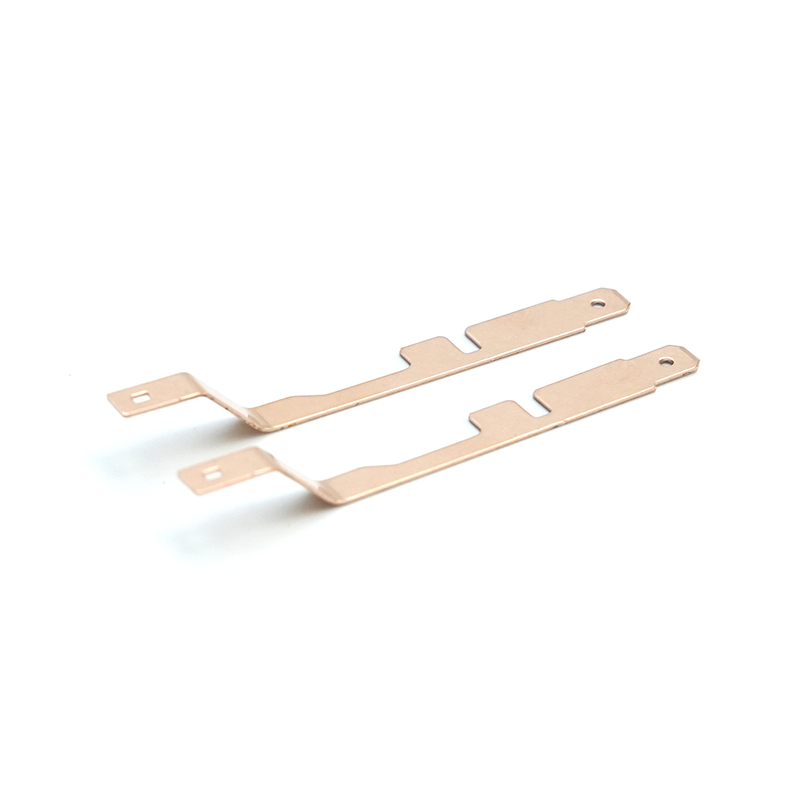
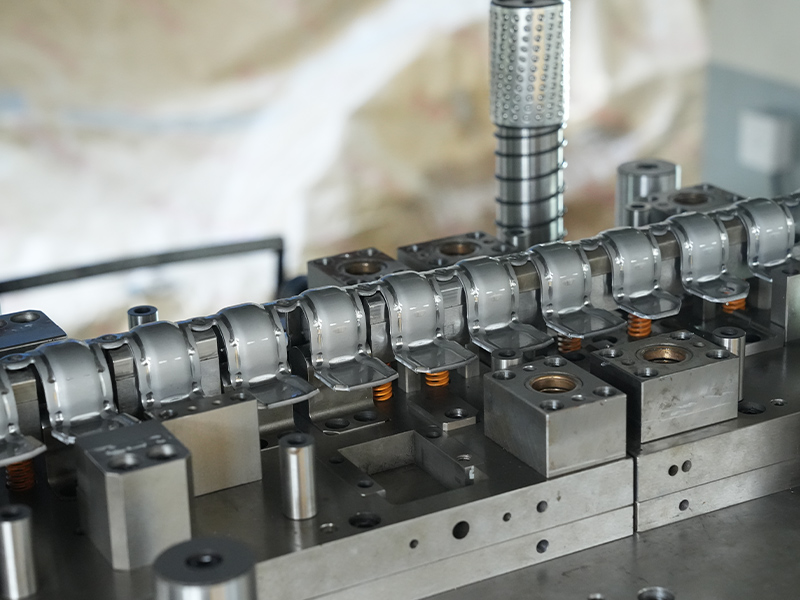
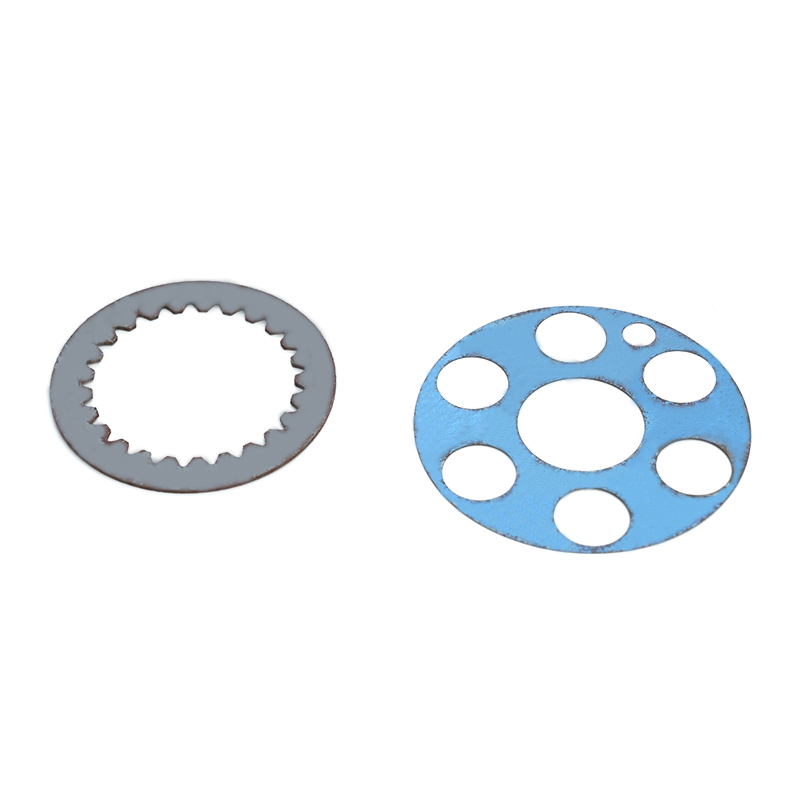
Copper stamping parts are widely used across various industries due to their excellent electrical conductivity, thermal resistance, and corrosion resistance. These precision components are manufactured through a metal forming process called stamping, where copper sheets are pressed into specific shapes using dies and punches.
This article explores the benefits, applications, manufacturing process, and key considerations for selecting copper stamping parts. We’ll also provide insights into industry trends and quality standards to help you make informed decisions.
Advantages of Copper Stamping Parts
Copper is a preferred material for stamped parts because of its unique properties:
- High Electrical Conductivity – Ideal for electrical connectors, terminals, and busbars.
- Excellent Thermal Conductivity – Used in heat sinks and cooling components.
- Corrosion Resistance – Suitable for harsh environments.
- Malleability & Ductility – Easily formed into complex shapes without cracking.
- Longevity – Resistant to wear, ensuring durability in high-use applications.
Common Applications of Copper Stamping Parts
Copper stampings are essential in multiple industries:
| Industry | Applications |
| Electronics | Connectors, terminals, relays, switches, circuit breakers. |
| Automotive | Battery contacts, sensors, fuse boxes, wiring harness components. |
| Renewable Energy | Solar panel connectors, inverter components, wind turbine electrical systems. |
| Telecommunications | RF shielding, antenna components, signal transmission parts. |
| Medical Devices | Precision electrodes, diagnostic equipment components. |
Manufacturing Process of Copper Stamping Parts
The production of high-quality copper stampings involves several steps:
1. Material Selection
- Pure copper (C11000) for high conductivity.
- Copper alloys (brass, bronze) for enhanced strength and corrosion resistance.
2. Blanking
- Sheets are cut into smaller blanks before forming.
3. Stamping/Forming
- Dies shape the copper into the desired form through punching, bending, or deep drawing.
4. Finishing
- Deburring, plating (tin, nickel, or silver), or annealing for improved performance.
5. Quality Inspection
- Dimensional checks, conductivity tests, and stress tests ensure reliability.

Key Considerations When Choosing Copper Stamping Parts
To ensure optimal performance, consider the following factors:
1. Material Grade
- Electrolytic Tough Pitch (ETP) Copper (C11000): Best for electrical applications.
- Copper Alloys (C26000 Brass, C51000 Phosphor Bronze): Used where strength and wear resistance are critical.
2. Precision & Tolerances
- Tight tolerances (±0.05mm) are necessary for high-performance electronics.
3. Surface Finish
- Plating (tin, nickel, or gold) may be required for corrosion resistance or solderability.
4. Production Volume
- Progressive die stamping for high-volume orders.
- Tool-and-die methods for custom, low-volume parts.
Industry Trends in Copper Stamping
- Miniaturization – Demand for smaller, high-precision components in electronics.
- Sustainable Manufacturing – Increased use of recycled copper.
- Automation – CNC and robotic stamping improve efficiency and consistency.
- High-Frequency Applications – 5G and IoT devices require advanced copper stampings.
Quality Standards for Copper Stamped Parts
To ensure reliability, manufacturers adhere to industry standards such as:
- ASTM B370 (Copper Sheet/Strip for Electrical Applications)
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems)
- RoHS & REACH Compliance (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
Conclusion
Copper stamping parts play a crucial role in modern industries, offering unmatched conductivity, durability, and versatility. Whether for electronics, automotive, or renewable energy applications, selecting the right material, precision level, and manufacturing process is key to performance.
By understanding the production methods, applications, and industry trends, businesses can make informed decisions when sourcing copper stampings. As technology advances, the demand for high-quality, precision-engineered copper components will continue to grow.