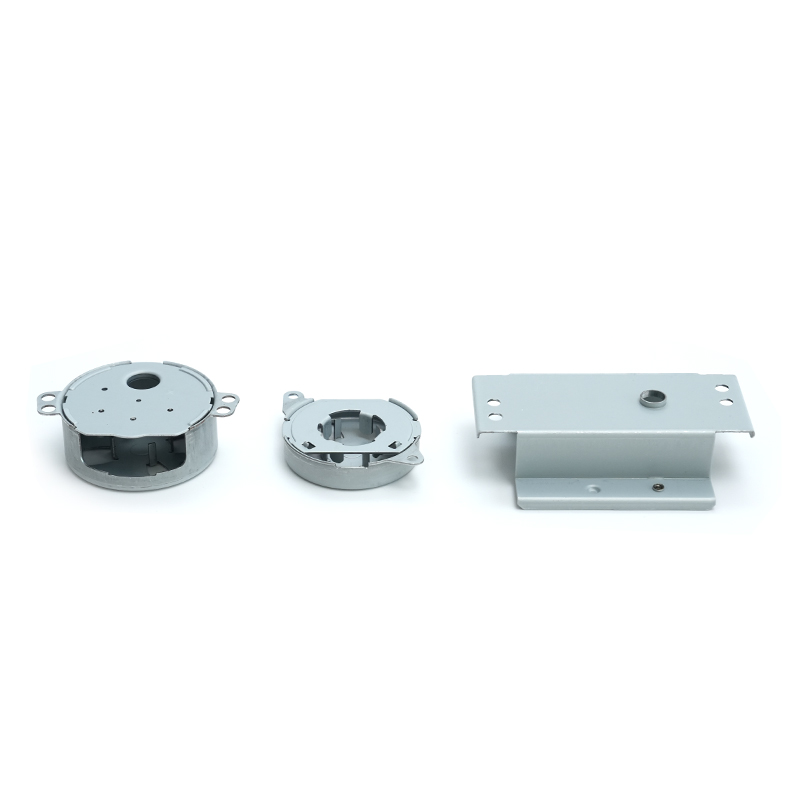
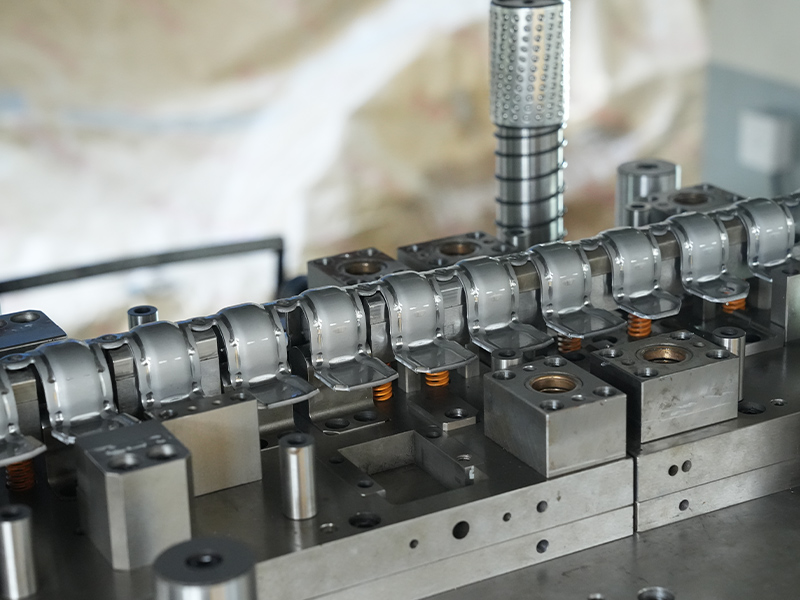
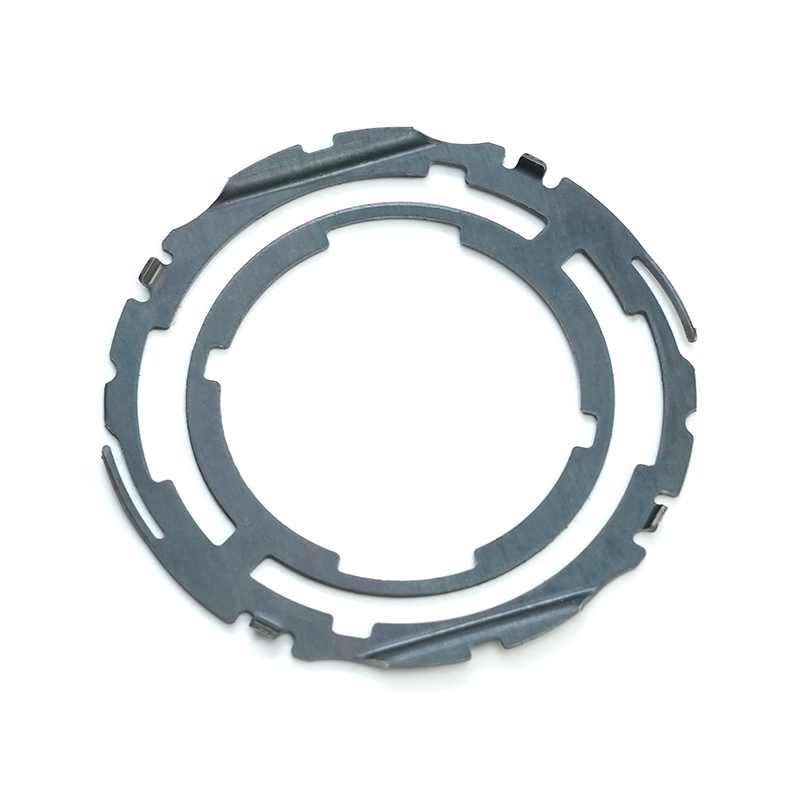
Aluminum stamping parts are essential components in numerous industries, offering lightweight durability and excellent corrosion resistance. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about aluminum metal stamping, from manufacturing processes to real-world applications.
What Are Aluminum Stamping Parts?
Aluminum stamping refers to the metalworking process where aluminum sheets or coils are formed into specific shapes using stamping presses and precision dies. These components are widely used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods industries due to aluminum's unique properties.
Aluminum Stamping Process Overview
The aluminum stamping manufacturing process typically involves these key stages:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right aluminum alloy (1100, 3003, 5052, 6061, etc.)
- Blanking: Cutting the aluminum sheet into smaller pieces
- Forming: Shaping the aluminum using dies and presses
- Piercing: Creating holes or cutouts in the material
- Bending: Forming angles and complex geometries
- Finishing: Applying surface treatments if required
Common Aluminum Grades for Stamping
| Aluminum Grade | Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 1100 | Excellent formability, high thermal conductivity | Heat exchangers, cookware |
| 3003 | Good strength, excellent corrosion resistance | Decorative trim, fuel tanks |
| 5052 | Highest strength of non-heat treatable alloys | Marine components, electronic chassis |
| 6061 | Heat treatable, good mechanical properties | Aerospace parts, structural components |
Key Advantages of Aluminum Stamping Parts
Aluminum stamping offers numerous benefits that make it preferable to other metal forming methods:
Lightweight Properties
Aluminum is about one-third the weight of steel, making stamped aluminum parts ideal for weight-sensitive applications like automotive and aerospace components where reducing mass improves fuel efficiency.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, providing excellent corrosion resistance without requiring additional coatings in many environments.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Certain aluminum alloys offer strength comparable to some steels while maintaining significant weight advantages.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum's thermal properties make it ideal for heat sink components and other thermal management applications.
Cost-Effective Production
Stamping allows for high-volume production of aluminum parts with minimal material waste and efficient manufacturing cycles.
Design Flexibility
Aluminum stamping accommodates complex geometries and precise tolerances, enabling innovative part designs.
Applications of Aluminum Stamping Parts
Aluminum stamped components serve critical functions across diverse industries:
Automotive Industry
Modern vehicles incorporate hundreds of aluminum stamped parts including:
- Radiator components
- Transmission parts
- Brackets and mounts
- Electrical connectors
- Body panels and trim
Aerospace Applications
The aerospace sector relies on precision aluminum stamping for:
- Aircraft structural components
- Avionics enclosures
- Seat frames
- Lighting components

Electronics and Electrical
Aluminum stamping produces essential electronic components such as:
- Heat sinks
- Shielding enclosures
- Connector housings
- Battery components
Consumer Goods
Everyday products containing aluminum stamped parts include:
- Appliance components
- Cookware
- Furniture hardware
- Decorative trim
Design Considerations for Aluminum Stamping
Successful aluminum stamping projects require careful attention to several design factors:
Material Thickness Selection
Choosing the appropriate aluminum thickness impacts both part strength and manufacturability. Thinner gauges allow for more complex forming but may lack required rigidity.
Bend Radius Guidelines
Aluminum typically requires larger bend radii than steel to prevent cracking. The minimum bend radius depends on the specific alloy and temper.
Tolerance Requirements
Establishing realistic tolerances ensures manufacturability while meeting functional requirements. Tighter tolerances increase tooling costs and may require secondary operations.
Surface Finish Specifications
Determine whether the stamped part requires special surface treatments like anodizing, painting, or powder coating for aesthetic or functional purposes.
Common Challenges in Aluminum Stamping
While aluminum offers many advantages, manufacturers must address certain challenges:
Springback Effect
Aluminum's elastic properties cause formed parts to partially return to their original shape after stamping, requiring compensation in tool design.
Gallling and Sticking
Aluminum's softness can cause material to stick to dies, necessitating proper lubrication and tool surface treatments.
Edge Cracking
Improper blanking or forming can lead to edge fractures, particularly with certain aluminum alloys and tempers.
Quality Control in Aluminum Stamping
Ensuring consistent quality requires multiple verification methods:
- First-article inspection
- Dimensional verification
- Material certification
- Surface finish evaluation
- Functional testing
Cost Factors in Aluminum Stamping
Several variables influence the cost of aluminum stamped parts:
Material Costs
Aluminum prices fluctuate based on market conditions and alloy specifications. Premium alloys command higher prices.
Tooling Investment
Stamping dies represent significant upfront costs but become economical at higher production volumes.
Production Volume
Higher quantities typically reduce per-unit costs through amortization of tooling and setup expenses.
Secondary Operations
Additional processes like machining, welding, or surface treatments increase overall part cost.
Future Trends in Aluminum Stamping
The aluminum stamping industry continues to evolve with several emerging developments:
Advanced Alloy Development
New aluminum formulations offer improved strength and formability characteristics for demanding applications.
Smart Manufacturing Integration
Industry 4.0 technologies enable real-time monitoring and optimization of stamping processes.
Sustainable Practices
Increased focus on recycling and energy-efficient production methods reduces environmental impact.
Conclusion
Aluminum stamping parts provide an optimal combination of lightweight performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness for numerous industrial applications. By understanding the material properties, manufacturing processes, and design considerations, engineers and purchasers can make informed decisions when specifying aluminum stamped components. As technology advances, aluminum stamping will continue to play a vital role in product development across multiple sectors.